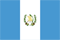
Varicose veins in the legs (Varicose veins - a common name) - Externally noticeable enlargement of the saphenous veins, which develops as a result of varicose veins or postthrombotic syndrome and is accompanied by a sharp violation of venous outflow in the lower extremities.
Modern methods allow radical treatment of varicose veins without wounds and pain.
Complaints with varicose veins
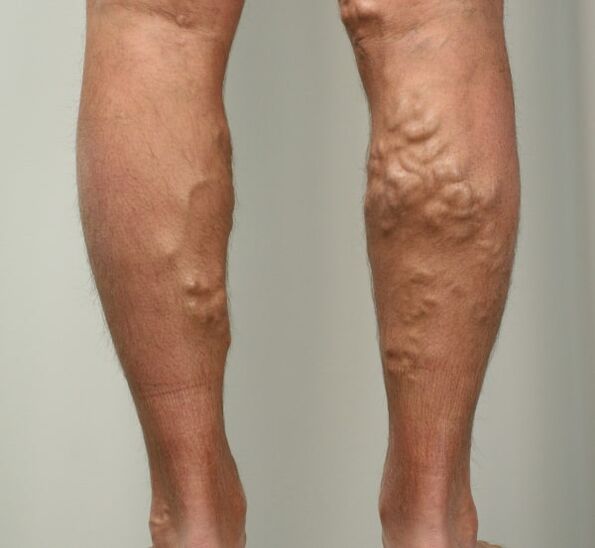
For many people, varicose veins and spider veins are just a cosmetic problem. In others, varicose veins cause excruciating pain and discomfort. Sometimes varicose veins cause more serious problems and complications - thrombophlebitis or trophic ulcers. Treatment involves removing or closing the deformed veins, which is the job of a phlebologist.
Varicose veins are complete degeneration of the venous wall associated with weakness of its connective tissue (varicose veins of the lower extremities) or develops with a severe disruption of venous outflow due to blockage or overheating of the veins.
Causes of varicose veins of the lower extremities
Varicose veins of the lower extremities
Disease as a cause of varicose veins of the legs is found in 20-40% of the population of developed countries. For a long time, varicose veins are just a cosmetic defect, but disease progression causes pain, swelling of the feet and legs, and in the advanced stage, darkening of the skin of the feet, inflammatory changes, and varicose trophic ulcers.
The main cause of primary varicose veins is hereditary predisposition, however the disease develops with excessive stress on the veins. The causative mechanism of varicose veins of the lower extremities is abrupt physical overload, pregnancy and childbirth. In this case there is a sharp increase in pressure in the veins of the lower extremities and damage to the valve apparatus, which triggers the mechanism of disease development.
Postthrombophlebitis
Secondary varicose veins develop after venous thrombosis or as a result of congenital diseases (arteriovenous fistulas, congenital venous dysplasia). Postthrombotic disease is a complex progressive pathological process in the venous system of the lower extremities. Due to valvular insufficiency or deep vein blockage, the saphenous veins dilate as they fill with blood. Another cause may be congenital or acquired arteriovenous fistulas. Occasionally there is a congenital obstruction of the deep veins, leading to secondary varicose veins (Klippel-Trenown syndrome).
Complications of varicose veins
More than 40% of women and 20% of men have varicose veins. In 20% of cases, varicose veins cause trophic ulcers, more than 25% of patients suffer from varicose vein thrombophlebitis. These complications often require serious treatment and pose a great threat to health.
Chronic venous insufficiency
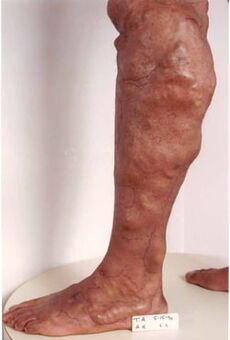
Venous outflow obstruction causes a pathological condition called chronic venous insufficiency. At the beginning of the disease may appear the appearance of individual nodules of varicose veins, which are not of great concern, although sometimes they can be painful. The number of varicose veins further increases. The disease progresses slowly but steadily. If the first varicose veins appeared below the knee, then the rate of disease development is much higher. If the disease has not stopped, then the third stage of venous insufficiency gradually develops. The swelling becomes permanent, a dark discoloration of the skin appears around the ankle, the heaviness in the legs is constantly bothering, which can continue even after a night of rest. Varicose veins thrombophlebitis and inflammation of the skin, eczema and dermatitis often develop. The last stage in the development of varicose veins is the appearance of trophic ulcers.
Thrombophlebitis of varicose veins
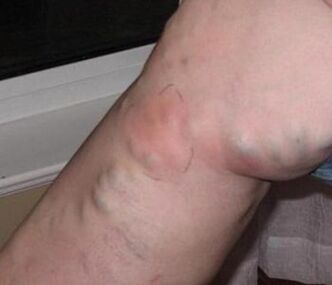
Thrombophlebitis of varicose veins MostIs a common complication. Thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of the venous wall, causing blood clots to form in the venous lumen. Thrombophlebitis develops in superficial and deep veins. Thrombophlebitis in varicose veins occurs in 25% of patients and is usually superficial. The cause of thrombophlebitis in varicose veins is very slow blood flow, especially in large nodes. Under these conditions, any factor that enhances blood clotting (pregnancy, overheating, trauma, sprains, hypothermia and scratches, acute respiratory infections) can cause a thrombus to form in a varicose vein and cause inflammation. Thrombophlebitis occurs in 25% of patients. With varicose veins of the lower extremities. The cause of thrombophlebitis is a slowing of blood flow in the varicose veins. Thrombophlebitis can progress and cause deep vein thrombosis. Chronic venous insufficiency is a painful condition of venous outflow through varicose veins. Characterized by swelling, darkening of the skin, the appearance of trophic ulcers and varicose dermatitis.
Varicose trophic ulcer

Trophic ulcer is a sign of extreme degree of chronic venous insufficiency. It is a long-term non-healing wound that results from severe disruption of venous outflow through deep and superficial veins. It is found in 1% of the general population and in 20% of patients with venous disease. One in five patients with varicose veins who do not receive treatment sooner or later develop a trophic ulcer. It can develop in both varicose veins and secondary varicose veins. Without eliminating abnormal venous discharge, varicose trophic ulcers will not heal, or recur permanently. Trophic ulcers of varicose veins occur in most patients and cause severe suffering. Modern minimally invasive methods allow you to reliably eliminate varicose trophic ulcers without wounds and pain.
Venous thrombosis and thromboembolism
Pulmonary embolism is a severe complication of venous thrombosis. Varicose veins are a significant risk factor for thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis. Thromboembolism leads to the development of severe heart and respiratory failure, with a mortality rate of more than 50%.
Prevention of varicose veins of the lower extremities
Any modern person should understand what varicose veins are in the legs, how to treat them and prevent its occurrence. With hereditary predisposition, factors contributing to varicose veins should be avoided. The use of venotonic preparations, wearing compression stockings during exercise, periodic examinations by a phlebologist, and venous ultrasound are shown.
When working under accompanying factors it is essential to use 1st compression class compression stockings at work, therapeutic exercises, outdoor activities, daily walks for at least 1 hour in medical socks, foot massage and swimming. Refuse to use complicated hereditary oral contraceptives for varicose veins. It is better to follow these simple rules than to treat varicose veins in the legs.
Avoid triggers during strenuous physical work. Compression stockings are necessary for this, especially those prone to varicose veins. Medical knitwear is indicated for all pregnant women, and in case of prone to varicose veins and thrombophlebitis, special compression stockings are worn for childbirth. It is advisable for all pregnant women to consult a phlebologist and have a venous ultrasound in the last weeks of pregnancy. This will help reduce the risk of venous system problems.
How to treat varicose veins in the legs
In the last 10 years, "barbaric" methods of treating varicose veins are a thing of the past, thanks to the emergence of more gentle and effective methods that have been used successfully in clinics.
Venous sclerotherapy for varicose veins
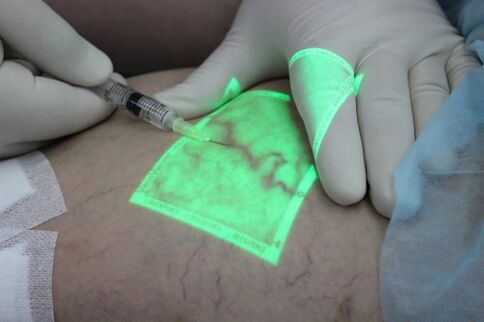
Sclerotherapy is the insertion of a drug into a varicose vein lumen that causes the walls to "stick together" with the disappearance of the veins. Currently, foam sclerotherapy is used to remove medium diameter varicose veins after laser obliteration of abnormal venous discharge. Sclerotherapy is indispensable for the treatment of spider veins and reticular varicose veins where it has no real competitors.
Laser treatment of varicose veins
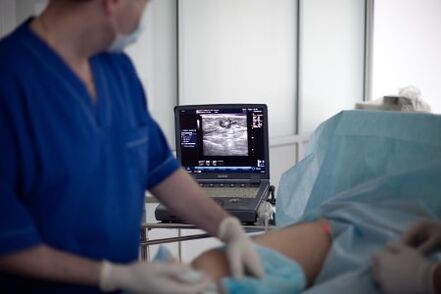
Laser treatment of varicose veins of the lower extremities (EVLT) is the most modern, radical and inexpensive method of treatment, which allows you to treat varicose veins in the legs, as well as to eliminate the causes of trophic ulcers. The importance of laser treatment lies in the thermal heating of the inside of the venous wall and the subsequent resorption of the varicose vein. The latest achievement of EVLT is the 1470 nm laser and radial light guide introduced into medical practice by phlebologists. The postoperative period after this technique is completely painless, and the result surpasses other treatment options - the radicality of the laser intervention is at least 98%.
Surgery to remove varicose veins
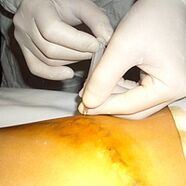
Surgical treatment of varicose veins with removal of major venous stems is a thing of the past. The risk of complications from stem vein removal has forced phlebologists to seek other approaches, leading to the development of laser techniques and other methods of thermal vein obliteration. However, the microbelectomy modification of classical phlebectomy according to Müller and Varad allowed a wonderful combination of laser treatment and removal of large varicose veins through puncture without wounds and sutures. The Varada technique saved patients from painful sclerotherapy of large varicose veins. Miniphlebectomy allows you to treat both varicose veins of the leg as well as removal of visible varicose veins anywhere on the body.
Radiofrequency obliteration of varicose veins
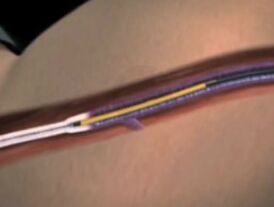
Radiofrequency ablation (RFO) of varicose veins of the legs is a modern and safe method of treatment. The method is based on the use of microwaves that heat a metal probe that is already in the vein wall and cause the destruction of the inner membrane. In terms of painlessness the method corresponds to laser coagulation with lasers at a wavelength of 1470 nm, its execution is simple and postoperative pain is small. However, RFO lags far behind laser in terms of long-term treatment outcomes. The efficiency of RFO is 85% without recurrence. The method is not suitable for the treatment of perforated veins.
Massage and bath for varicose veins
Massage is a method of active treatment of varicose veins.
Used in all types of modern massage, especially in pathology of the lymphatic and venous systems. Among the exclusive methods is the technology of lymphatic drainage massage with a bandage, which is very effective in relieving chronic venous insufficiency.
In chronic venous insufficiency, massage is used to eliminate venous hypertension in varicose veins and post-thrombotic syndrome. The combination of this massage with a bandage allows you to effectively eliminate all clinical manifestations of the disease.
A bath with varicose veins, thrombophlebitis or post-thrombotic disease is very dangerous. Any thermal stress can cause deep vein blood clots to form with all subsequent consequences.
Unfortunately, complete cure of varicose veins is impossible without eliminating venous discharge and varicose veins. Although the reduction of symptoms associated with venous blood stagnation in the legs is quite possible with the help of modern therapy. However, the spread of varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency sometimes raises the desire to speculate on this problem. Consider modern methods of treatment and nonsense.
Remedies for varicose veins
The goal of venous pathology medication therapy is to reduce symptoms and prevent complications, but achieving these goals is not easy. The abundance of tools used today has raised another problem: which one to choose? Unfortunately, most of the proposed drugs have quite low efficacy, despite the theoretically justified expediency of their use. This is due to a number of reasons, the main of which is the low absorption of the healing substances of these drugs by the body. The ideal drug for the treatment of venous insufficiency should act as much as possible on the pathogenetic link in chronic venous insufficiency with minimal side effects and high absorption by the body. Quite a large number of venotonics are represented in the modern pharmaceutical market. However, they have similar medicinal substances (herbal flavonoids) and therefore the effectiveness of one or the other depends only on the concentration and digestion of the active principle.
You should not expect varicose veins to disappear from these drugs, however there may be lightness in the legs, reduced swelling and disappearance of night cramps.
Creams and gels for varicose veins
Despite the high efficiencies promoted by vendors and manufacturers, creams and gels do not relieve varicose veins and varicose veins do not disappear from them. In the early stages of venous insufficiency, phlebologists do not object to the use of these remedies because their burning promotes venous outflow as a light massage and has a calming effect on the skin. With advanced forms of venous insufficiency, these creams and ointments can cause dermatitis and allergies and are therefore very harmful. Some drugs are used in the development of acute thrombophlebitis and help to calm the inflammatory process, but varicose veins do not disappear from them. Thanks to the right advertising, shamanic products with fleas have gained great popularity among the people, but they have no attitude towards medicines and expectations from them do not make sense.
Remedies for blood clots in varicose veins
A common complication of varicose veins is thrombophlebitis, especially during pregnancy and postpartum. A proven drug for the prevention of blood clots is glycosaminoglycan containing low molecular weight acid sulfur. Tablets are used in clinics to prevent thrombophlebitis after treatment of varicose veins. They are taken 7 days after laser or radiofrequency intervention.
Compression stockings for varicose veins

Compression garment tissue is undoubtedly one of the most effective means of treating venous edema and reducing the degree of chronic venous insufficiency. Invented more than 100 years ago, after gaining great popularity in the 20th and even more so in the 21st century, compression socks and stockings have become an integral part of phlebologist treatment. This is due to the effects it has:
- Improving venous and lymphatic drainage from the lower extremities,
- Improving microcirculation,
- Slowing disease progression;
- Prevention of varicose vein complications (varicothrombophlebitis, trophic disorders),
- Prevention of deep vein thrombosis.
How to use compression socks
So if you have varicose veins and are planning to treat it, then you will undoubtedly use compression stockings for a few days or months (individually) during treatment. If your feet become swollen at the end of the day after work and you suffer from severe leg syndrome, you can use compression stockings during the day to avoid these symptoms in the evening. If you have untreated varicose vein complications - trophic ulcers or thrombophlebitis - you are certainly using compression to improve the condition of the legs and reduce the unpleasant symptoms.
The fact is that by improving venous outflow, compression stockings are worn every second to improve venous blood flow from the legs, which is undoubtedly not easy for disease-damaged veins and against the law of universal gravity. Compression knitwear can safely be called one of the genius inventions of mankind, but in order for it to work for you, a few conditions must be met:
- Compression knitwear is selected individually (according to standards). The main requirement is to conform to the anatomical profile of the limb and therefore to create the correct pressure gradient.
- Knitted clothes are selected by the doctor (phlebologist) individually. Medicinal products are denoted in mm Hg and are divided into compression classes 1, 2, 3, 4. Each class of compression corresponds to a certain pressure. The appropriate class of compression is used at different stages of varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency. That is why only a doctor has the right to prescribe and choose the right compression stockings - taking into account the nature of the pathology and according to individual standards.
- It should be medical and not slimming woven. Only RAL certified brands.
When do you need knitted clothes for varicose veins?
- Correction of "heavy legs" syndrome: reduction of severity, edema, improvement of quality of life;
- During treatment with a phlebologist: after surgery or for a period prescribed by a specialist;
- Slowing the progression of varicose veins;
- For the treatment of complications of varicose veins (varicothrombophlebitis).
An essential component of any treatment for varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency is medical elastic compression. Thanks to compression therapy it is possible to completely eliminate the swelling, heaviness in the legs and create conditions for any kind of radical treatment of varicose veins. Modern medical woven clothing has a high therapeutic effect and excellent aesthetic properties.
Elastic bandages |
Therapeutic T-shirt |
|---|---|
Creating the necessary pressure is determined by the physician and patient bandaging techniques and skills |
The processing profile and pressure level are indicated according to the compression class during production |
The need for medical participation in bandaging or patient education |
Physician participation is limited to selecting the compression class and product type |
Difficulties in providing compression and fixation on the thigh |
Provides effective compression and fixation on the thigh |
Used for non-standard shape of the limb |
Personalization is possible through non-standard shape of the limb |
Daily washing causes rapid wear of the bandages |
Daily washing is essential to maintain compression properties |
Needs replacement after several washes |
Guaranteed maintenance of compression properties for 6 months |
Possible disturbance of skin water and temperature balance |
The porous package ensures normal skin temperature and water balance |
Low aesthetic properties, provides convenience and comfort |
High aesthetic properties, convenience and comfort when used |
Exercises and sports for varicose veins
Strength sports for varicose veins and athletics are possible after the elimination of varicose syndrome, or in compression stockings of 2-3 compression class. Modern treatment can return the legs with varicose veins to normal condition, which removes all the restrictions.
We present to your attention a set of therapeutic and prophylactic exercises developed by leading experts. Its regular implementation will help reduce the incidence of venous insufficiency in the lower extremities, slow the progression of the disease and the risk of life-threatening complications.
- Unloading the leg veins. Breathe deeply and evenly, start with your eyes closed, relax. At the same time, place a few pillows under your feet so that they are raised at an angle of 15-20 °.
- In bicycle training. Lying on your back and breathing evenly Imagine riding a bicycle with pedals.
- The exercise consists of several parts, performed slowly and smoothly. Start with your legs spread on your back, take a deep breath. Exhale, bend the right leg, bring the knee to the chest. When inhaling, straighten the leg vertically upwards. Exhale, lower it. Repeat this exercise alternately for each leg.
- Lie on your back, arms across your body, lift your legs vertically upwards. Rotate both legs inward, then outward at the same time.
- Alternately bend and spread your legs back and forth at the ankle joint.
- Bend alternately and spread the toes.
- Stand in a posture: legs together, hands along the body. After a deep breath, slowly lift your fingers, exhale, return to the starting position.
- Walk on the ground without lifting socks off the floor.
- Vertical scissors. Lying on your back, arms across your body, breathing evenly, alternately crossing your legs, alternately.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees without lifting your legs off the floor. Put your hands on your hips. Inhale slowly, lift your head and torso. At the same time, the hands slide to the knees. Exhale slowly, return to starting position.
- Lie on your back, hands along the body, legs at an angle of 15-20 °, hold a small pillow between the legs. Inhale slowly, lean on the waist, remove the buttocks from the mattress. Exhale slowly, return to starting position.
- Lie on your back, arms across your body, knees bent, feet flat on the floor. Exhale slowly, insert into the abdomen. Inhale slowly, inflate the stomach.
- Lie on your back, legs at an angle of 15-20 °. Bend the right leg, bring the knee to the chest. At the same time, bend the leg tightly with your hands. Slowly straighten your leg up. Hands, gripping the leg tightly, slide along the calf at knee level. Slowly lower your leg, sliding your hands over your thighs. The exercise is repeated for the second leg.
- Stand, feet together, hands across the body, inhale slowly, shoulders back, exhale slowly, rest the shoulders and lean your head forward.
- Contrasting shower on the feet. Interchangeable solid cannons for warm and cool water. 5-10 minutes for each foot.